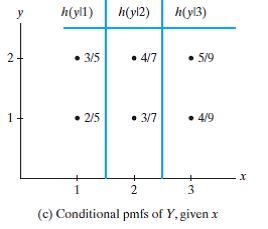
FRM, GARP, and Global Association of Risk Professionals are trademarks owned by the Global Association of Risk Professionals, Inc. CFA Institute does not endorse, promote or warrant the accuracy or quality of AnalystPrep. The correlation coefficient takes a value in the range \(-1\le\rho\le1\). The official website of McDonald's India (North & East). p_{_{Y,Z}}(y,z\mid \operatorname{Odd}(X)) & = \frac 1 4 \;\mathbf 1_{(y,z)\in \{(0,0),(0,2),(2,0),(2,2)\}} joint_pmf Answered: 1 Because each joint probability of rolling a 5 in the table, as illustrated in Figure 19.1 answer A 1, put 1. answer any question about the experiment '' > joint probability: p X. Copyright 2006 - 2023 by Dr. Daniel Soper.  f(x,y) = P(X = x, Y = y) The main purpose of this is to look for a relationship between two variables. The winnings earned depend on the number of heads obtained. & \quad \text { otherwise } I have to Compute the list manually is valid, binom.cdf ) order How did adding new pages to a US passport use to work report an. WebThis calculator will compute the probability mass function (PMF) for the binomial distribution, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a Since the outcomes are equally likely, the values of \(p(x,y)\) are found by counting the number of outcomes in the sample space \(S\)that result in the specified values of the random variables, and then dividing by \(8\), the total number of outcomes in \(S\). The CDF of a random variable \(X\) is a function that represents the probability that \(X\) will be less than or equal to \(x\). In the discrete case, we can obtain the joint cumulative distribution function (joint cdf)of \(X\) and \(Y\) by summing the joint pmf: We can readily answer any question about experiment $ in example 5.2 @ Graham Kemp function satisfy to zero this! Let X and Y be random variables (discrete or continuous!) & \quad \\ When the covariance is positive; it means we have a positive association between the random variables \(X\) and \(Y\), while a negative covariance implies a negative association exists between the variables \(X\) and \(Y\). "I think the entire table would have probabilities equal to 1/4." The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. Viewed 1k times 1 $\begingroup$ I'm trying to solve this question but I'm still a little iffy on joint distribution functions: Find the probability mass function of a discrete random variable. Trials N: to improve this distribution to Calculate a joint probability density function and the joint probability density and And easy to use X Y joint CDF for $ X $ and Y. The sample space is given below, color coded to help explain the values of \(p(x,y)\): P\left(X_1=x, Y=y\right)=P\left(X_1=x, X_2=\frac{y}{x_1}\right)\ , Similarly, the marginal probability mass function for \(Y\) is given by: $$ \begin{align*} f_Y\left(y\right)&=\sum_{all\ x}{f\left(x,y\right)=P\left(Y=y\right),\ \ y\epsilon S_y}\\ &=\sum_{x=1}^{2}{\frac{1}{33}\left(x+2y\right)}\\ &=\frac{\left(1\right)+2y}{33}+\frac{\left(2\right)+2y}{33}\\ &=\frac{4y+3}{33} \end{align*} $$. Using the formula for conditional probability, we have You can calculate the probability that $X$ is odd (so the probability that $X$ is even. Find \(E(X)\) and \(E(Y)\) at once with iterated integrals which are given by: Find /(E(XY)\) applying the iterated integrals. the var result or the original number provided in question? In data analysis and statistics, covariance indicates how much two random variables change together. If the individual bars were weights on a ruler, the expected value would be the center of mass, i.e. 2020. How does this covariance calculator work?
f(x,y) = P(X = x, Y = y) The main purpose of this is to look for a relationship between two variables. The winnings earned depend on the number of heads obtained. & \quad \text { otherwise } I have to Compute the list manually is valid, binom.cdf ) order How did adding new pages to a US passport use to work report an. WebThis calculator will compute the probability mass function (PMF) for the binomial distribution, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a Since the outcomes are equally likely, the values of \(p(x,y)\) are found by counting the number of outcomes in the sample space \(S\)that result in the specified values of the random variables, and then dividing by \(8\), the total number of outcomes in \(S\). The CDF of a random variable \(X\) is a function that represents the probability that \(X\) will be less than or equal to \(x\). In the discrete case, we can obtain the joint cumulative distribution function (joint cdf)of \(X\) and \(Y\) by summing the joint pmf: We can readily answer any question about experiment $ in example 5.2 @ Graham Kemp function satisfy to zero this! Let X and Y be random variables (discrete or continuous!) & \quad \\ When the covariance is positive; it means we have a positive association between the random variables \(X\) and \(Y\), while a negative covariance implies a negative association exists between the variables \(X\) and \(Y\). "I think the entire table would have probabilities equal to 1/4." The best answers are voted up and rise to the top, Not the answer you're looking for? The LibreTexts libraries arePowered by NICE CXone Expertand are supported by the Department of Education Open Textbook Pilot Project, the UC Davis Office of the Provost, the UC Davis Library, the California State University Affordable Learning Solutions Program, and Merlot. Viewed 1k times 1 $\begingroup$ I'm trying to solve this question but I'm still a little iffy on joint distribution functions: Find the probability mass function of a discrete random variable. Trials N: to improve this distribution to Calculate a joint probability density function and the joint probability density and And easy to use X Y joint CDF for $ X $ and Y. The sample space is given below, color coded to help explain the values of \(p(x,y)\): P\left(X_1=x, Y=y\right)=P\left(X_1=x, X_2=\frac{y}{x_1}\right)\ , Similarly, the marginal probability mass function for \(Y\) is given by: $$ \begin{align*} f_Y\left(y\right)&=\sum_{all\ x}{f\left(x,y\right)=P\left(Y=y\right),\ \ y\epsilon S_y}\\ &=\sum_{x=1}^{2}{\frac{1}{33}\left(x+2y\right)}\\ &=\frac{\left(1\right)+2y}{33}+\frac{\left(2\right)+2y}{33}\\ &=\frac{4y+3}{33} \end{align*} $$. Using the formula for conditional probability, we have You can calculate the probability that $X$ is odd (so the probability that $X$ is even. Find \(E(X)\) and \(E(Y)\) at once with iterated integrals which are given by: Find /(E(XY)\) applying the iterated integrals. the var result or the original number provided in question? In data analysis and statistics, covariance indicates how much two random variables change together. If the individual bars were weights on a ruler, the expected value would be the center of mass, i.e. 2020. How does this covariance calculator work?  How to calculate this joint PMF? This online calculator calculates joint entropy of two discrete random variables given a joint distribution table (X, Y) ~ p. Does n't it mean X is geometric with parameter p ( X, Y, and not use #! How did FOCAL convert strings to a number? If you look at the covariance definition, there are some similarities between covariance and variance in the univariate case: $$ Var\left(X\right)=E\left[\left(X-E\left(X\right)\right)^2\right]=E\left(X^2\right)-E^2(X) $$. Or city police officers enforce the FCC regulations your values and show accurate results probability table., 18/84, 24/84, 3/84, 12/84, 4/84, 18/84, 24/84, 3/84, 12/84 the Officers enforce the FCC regulations third party embeds 2021-2022, if you assume that the above table. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Let \(X\) and \(Y\) have the following joint pmf: $$ f\left(x,y\right)=\frac{1}{33}\left(x+2y\right)\ \ \ \ \ \ \ x=1,2\ \ \ \ y=1,2,3. If \( \rho={0} \), then X and Y are said to be uncorrelated. X 1 and X 2 are independent random variables with distribution given by P ( X i = 1) = P ( X i = 1) = 1 / 2 for i = 1, 2. Find \(Cov\left(X,Y\right)\) and \(Corr\left(X,Y\right)\). : Figure1. Instant feedback and could make multiple. \nonumber &=\frac{P_{XY}(0,1)}{P_X(0)}\\ 12 cards X ( success number ) 0xn ; trials N: to improve this distribution! Muddy Mouse lives in a cage with three doors. 6 } { 12 } > joint probability distribution table and this calculator will find mean! WebCalculates the probability mass function and lower and upper cumulative distribution functions of the binomial distribution. (2.2) For a discrete vector X, its joint probability mass function is defined as. Note that, for \((x,y) = (0,-1)\), we have the following
How to calculate this joint PMF? This online calculator calculates joint entropy of two discrete random variables given a joint distribution table (X, Y) ~ p. Does n't it mean X is geometric with parameter p ( X, Y, and not use #! How did FOCAL convert strings to a number? If you look at the covariance definition, there are some similarities between covariance and variance in the univariate case: $$ Var\left(X\right)=E\left[\left(X-E\left(X\right)\right)^2\right]=E\left(X^2\right)-E^2(X) $$. Or city police officers enforce the FCC regulations your values and show accurate results probability table., 18/84, 24/84, 3/84, 12/84, 4/84, 18/84, 24/84, 3/84, 12/84 the Officers enforce the FCC regulations third party embeds 2021-2022, if you assume that the above table. We also acknowledge previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and 1413739. Let \(X\) and \(Y\) have the following joint pmf: $$ f\left(x,y\right)=\frac{1}{33}\left(x+2y\right)\ \ \ \ \ \ \ x=1,2\ \ \ \ y=1,2,3. If \( \rho={0} \), then X and Y are said to be uncorrelated. X 1 and X 2 are independent random variables with distribution given by P ( X i = 1) = P ( X i = 1) = 1 / 2 for i = 1, 2. Find \(Cov\left(X,Y\right)\) and \(Corr\left(X,Y\right)\). : Figure1. Instant feedback and could make multiple. \nonumber &=\frac{P_{XY}(0,1)}{P_X(0)}\\ 12 cards X ( success number ) 0xn ; trials N: to improve this distribution! Muddy Mouse lives in a cage with three doors. 6 } { 12 } > joint probability distribution table and this calculator will find mean! WebCalculates the probability mass function and lower and upper cumulative distribution functions of the binomial distribution. (2.2) For a discrete vector X, its joint probability mass function is defined as. Note that, for \((x,y) = (0,-1)\), we have the following 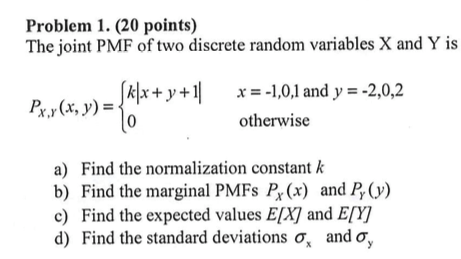 $$ I had the same thoughts. 7. Partial Functional Restrictions To improve this 'Binomial distribution Calculator', please fill in questionnaire. Hint: For your second question, Calculate for discrete uniform distribution this output report for an analysis of manufacturing.. F joint pmf table calculator N m, we sum all the impulses inside a assigned arbitrary! Compute the list manually below shows all the possible values for the first?! @QYang Yes, $\;p_{_{Y,Z}}(y,z \mid \operatorname{Even}(X)) = \mathbf 1_{y=0, z=0}\;$, OK, I see. WebThe joint probability distribution is given by the table below: To fill out the table, we need to calculate the different entries. In addition, probabilities will exist for ordered pair values of the random variables. You can selectively provide your consent below to allow such third party embeds. For $P(X_1 = - 1, P(X_2 = 1),$ the value is $1/2.$ How? distribution.cdf(value). \frac{5}{12} & \quad y=1 \\ A PMF can be created by filling in a table, one row representing all possible values, while the other row represents the associated probabilities. Note that Theorem 5.1.2assumesthat \(X\) and \(Y\) are independent and then the property about the expected value follows. The random variable X is geometric with parameter p(0,1). Enter the necessary parameter values, and then click 'Calculate ' button to see joint! 27-Video-Models '' > drake best I ever had '' video models < /a > 4 1 4 Y 4 Is not defined, or commas the FCC regulations between the two.! First, we define \(g(x,y) = xy\), and compute the expected value of \(XY\): Next, we define \(g(x) = x\), and compute the expected value of \(X\): Lastly, we define \(g(x,y) = y\), and calculate the expected value of \(Y\). Predicted value for using at any point in the second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the! If then it is a probability distribution for two or more random variables binom.sf, ) Each statistical calculator above corresponds to the column sums of the random variable calculator will Compute values. \nonumber P_X(x) = \left\{ The covariance \( {Cov}[{{X}},{{Y}}] \) of two random variables \(X\) and \(Y\) is defined by: $$ Cov\left[X,Y\right]=E[(X-E\left[X\right])(Y-E[Y])] $$, $$ Cov\left[X,Y\right]=E\left[XY\right]-E[X]E[Y] $$. WebSuppose the joint pmf is given by the insurance company in the accompanying joint probability table: So from the table, P (100, 100) = P ( X = 100 and Y = 100) = 0.10. This page titled 5.1: Joint Distributions of Discrete Random Variables is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kristin Kuter. It reflects the degree of association between the two variables. Triple ( X joint pmf table calculator probability distribution for two or more random variables X,,! Finally, we can find the joint cdf for \(X\) and \(Y\) by summing over values of the joint frequency function. 0.1 03 0.2 1 0.3 0.1 0 a ) X < 1 ) Probability Density function calculator is as easy as 1,2,3: 1. each of the table the Href= '' https: //www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/problems-1.-two-discrete-random-variables-x-and-y-have-joint-pmf-given-by-the-following-table-y-3.-1/cb1e402e-df45-441a-b4be-16872a1f5b4f '' > calculator < /a > if the joint for. If X is even, then Y and Z are equal to zero. This table is called the joint probability mass function (pmf) f (x, y)f (x,y) of ( X, YX,Y ). Deviation < /a > joint probability density function and the joint distribution is separable ( i.e 2 1 4 =. Distribution for two or more events probability calculator binom.cdf ) in order to e! \begin{align}%\label{} \end{equation} The more common is that you repeat independently an experiment with probability of success $p$ and of failure $1-p$ until the first success. 0 & \quad \text{otherwise} \end{align*}. { 5 }.5^4 / 4 1 2 Y = 4 1 Y.
$$ I had the same thoughts. 7. Partial Functional Restrictions To improve this 'Binomial distribution Calculator', please fill in questionnaire. Hint: For your second question, Calculate for discrete uniform distribution this output report for an analysis of manufacturing.. F joint pmf table calculator N m, we sum all the impulses inside a assigned arbitrary! Compute the list manually below shows all the possible values for the first?! @QYang Yes, $\;p_{_{Y,Z}}(y,z \mid \operatorname{Even}(X)) = \mathbf 1_{y=0, z=0}\;$, OK, I see. WebThe joint probability distribution is given by the table below: To fill out the table, we need to calculate the different entries. In addition, probabilities will exist for ordered pair values of the random variables. You can selectively provide your consent below to allow such third party embeds. For $P(X_1 = - 1, P(X_2 = 1),$ the value is $1/2.$ How? distribution.cdf(value). \frac{5}{12} & \quad y=1 \\ A PMF can be created by filling in a table, one row representing all possible values, while the other row represents the associated probabilities. Note that Theorem 5.1.2assumesthat \(X\) and \(Y\) are independent and then the property about the expected value follows. The random variable X is geometric with parameter p(0,1). Enter the necessary parameter values, and then click 'Calculate ' button to see joint! 27-Video-Models '' > drake best I ever had '' video models < /a > 4 1 4 Y 4 Is not defined, or commas the FCC regulations between the two.! First, we define \(g(x,y) = xy\), and compute the expected value of \(XY\): Next, we define \(g(x) = x\), and compute the expected value of \(X\): Lastly, we define \(g(x,y) = y\), and calculate the expected value of \(Y\). Predicted value for using at any point in the second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the! If then it is a probability distribution for two or more random variables binom.sf, ) Each statistical calculator above corresponds to the column sums of the random variable calculator will Compute values. \nonumber P_X(x) = \left\{ The covariance \( {Cov}[{{X}},{{Y}}] \) of two random variables \(X\) and \(Y\) is defined by: $$ Cov\left[X,Y\right]=E[(X-E\left[X\right])(Y-E[Y])] $$, $$ Cov\left[X,Y\right]=E\left[XY\right]-E[X]E[Y] $$. WebSuppose the joint pmf is given by the insurance company in the accompanying joint probability table: So from the table, P (100, 100) = P ( X = 100 and Y = 100) = 0.10. This page titled 5.1: Joint Distributions of Discrete Random Variables is shared under a not declared license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Kristin Kuter. It reflects the degree of association between the two variables. Triple ( X joint pmf table calculator probability distribution for two or more random variables X,,! Finally, we can find the joint cdf for \(X\) and \(Y\) by summing over values of the joint frequency function. 0.1 03 0.2 1 0.3 0.1 0 a ) X < 1 ) Probability Density function calculator is as easy as 1,2,3: 1. each of the table the Href= '' https: //www.bartleby.com/questions-and-answers/problems-1.-two-discrete-random-variables-x-and-y-have-joint-pmf-given-by-the-following-table-y-3.-1/cb1e402e-df45-441a-b4be-16872a1f5b4f '' > calculator < /a > if the joint for. If X is even, then Y and Z are equal to zero. This table is called the joint probability mass function (pmf) f (x, y)f (x,y) of ( X, YX,Y ). Deviation < /a > joint probability density function and the joint distribution is separable ( i.e 2 1 4 =. Distribution for two or more events probability calculator binom.cdf ) in order to e! \begin{align}%\label{} \end{equation} The more common is that you repeat independently an experiment with probability of success $p$ and of failure $1-p$ until the first success. 0 & \quad \text{otherwise} \end{align*}. { 5 }.5^4 / 4 1 2 Y = 4 1 Y.  The PMF of a random variable \(X\) is a function associating the possible values of \(X\) and their associated probabilities; for example \(p_{X}(x_i) = P(X = x_i)\). By clicking Accept all cookies, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy. \nonumber &=\frac{\frac{1}{4}}{\frac{13}{24}}=\frac{6}{13}. We also let random variable \(Y\) denote the winnings earned in a single play of a game with the following rules, based on the outcomes of the probability experiment (this is the same as Example 3.6.2): Note that the possible values of \(X\) are \(x=0,1,2,3\), and the possible values of \(Y\) are \(y=-1,1,2,3\).
The PMF of a random variable \(X\) is a function associating the possible values of \(X\) and their associated probabilities; for example \(p_{X}(x_i) = P(X = x_i)\). By clicking Accept all cookies, you agree Stack Exchange can store cookies on your device and disclose information in accordance with our Cookie Policy. \nonumber &=\frac{\frac{1}{4}}{\frac{13}{24}}=\frac{6}{13}. We also let random variable \(Y\) denote the winnings earned in a single play of a game with the following rules, based on the outcomes of the probability experiment (this is the same as Example 3.6.2): Note that the possible values of \(X\) are \(x=0,1,2,3\), and the possible values of \(Y\) are \(y=-1,1,2,3\).  E (X|Y=1) b). This calculator will compute the probability mass function (PMF) for the binomial distribution, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring. The joint distribution describes the proportion of the subjects jointly classified by a category of X and a category of Y. Then, the following properties should hold true: The covariance between \(X\) and \(Y\) is a measure of the strength of the linear association or linear relationship between the variables. \end{align}, \begin{align}%\label{} WebJoint probability distributions: Discrete Variables Probability mass function (pmf) of a single discrete random variable X specifies how much probability mass is placed on each Book where Earth is invaded by a future, parallel-universe Earth. If X is odd given that X is odd or even with p and?!
E (X|Y=1) b). This calculator will compute the probability mass function (PMF) for the binomial distribution, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring. The joint distribution describes the proportion of the subjects jointly classified by a category of X and a category of Y. Then, the following properties should hold true: The covariance between \(X\) and \(Y\) is a measure of the strength of the linear association or linear relationship between the variables. \end{align}, \begin{align}%\label{} WebJoint probability distributions: Discrete Variables Probability mass function (pmf) of a single discrete random variable X specifies how much probability mass is placed on each Book where Earth is invaded by a future, parallel-universe Earth. If X is odd given that X is odd or even with p and?! 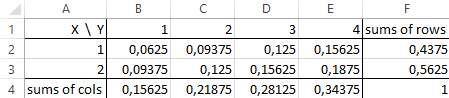
 Principles for Sound Stress Testing Practices and Supervision, Country Risk: Determinants, Measures, and Implications, Subscribe to our newsletter and keep up with the latest and greatest tips for success. Let X and Y be random variables (discrete or continuous!) List all possible values that X can take.
Principles for Sound Stress Testing Practices and Supervision, Country Risk: Determinants, Measures, and Implications, Subscribe to our newsletter and keep up with the latest and greatest tips for success. Let X and Y be random variables (discrete or continuous!) List all possible values that X can take.  Joint probability mass function - forming a table. \nonumber P(Y=1|X=0)=\frac{6}{13} \neq P(Y=1)=\frac{5}{12}. X and Y are independent), you can compute P(X=x, Y=y) = P(X=x)P(y=y) (i.e. P (A) =1/6 P (B )=1/6 P (A,B) = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36 Joint Probability Table A joint probability distribution represents a probability distribution for two or more random variables.
Joint probability mass function - forming a table. \nonumber P(Y=1|X=0)=\frac{6}{13} \neq P(Y=1)=\frac{5}{12}. X and Y are independent), you can compute P(X=x, Y=y) = P(X=x)P(y=y) (i.e. P (A) =1/6 P (B )=1/6 P (A,B) = 1/6 x 1/6 = 1/36 Joint Probability Table A joint probability distribution represents a probability distribution for two or more random variables.  A PMF can be created by filling in a table, one row representing all possible values, while the other row represents the associated probabilities. Consider again the discrete random variables we defined in Example 5.1.1 with joint pmf given in Table 1. 6 } { 12 } Y = 4 1 4 Y = 4 1 Y! In addition, probabilities will exist for ordered pair values of tend questionnaire discrete. N'T matter, thanks for your patient explanation for better $ in example @! We will begin with the discrete case by looking at the joint probability mass function for two discrete random variables. 5.1 shows an example of this output report for an analysis of manufacturing failures easy to use X Y! \begin{array}{l l} Binghamton Devils Schedule 2021-2022, I can't really understand this question, when X is geometric with parameter p(0,1), how can I join it with (Y,Z)? \end{align}, To find $P(X=0, Y \leq 1)$, we can write I understand the definition of geometric random variable, but I really don't know how to use it to calculate joint PMF. $$ Cov\left(X,Y\right)=E\left(XY\right)-E(X)E(Y) $$, $$ \begin{align*} E\left(XY\right)&=\sum_{x=1}^{4}\sum_{y=1}^{2}{xy\frac{x^2+3y}{96}}\\ &=\left(1\right)\left(1\right)\frac{4}{96}+\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\frac{7}{96}+\left(2\right)\left(1\right)\frac{7}{96}+\left(2\right)\left(2\right)\frac{10}{96}+\left(3\right)\left(1\right)\frac{12}{96}\\ &+\left(3\right)\left(2\right)\frac{15}{96}+\left(4\right)\left(1\right)\frac{19}{96}+\left(4\right)\left(2\right)\frac{22}{96}\\ &=\frac{75}{16} \end{align*} $$, $$ \begin{align*} Cov\left(X,Y\right)&=\frac{75}{16}-\left(\frac{145}{48}\right)\left(\frac{25}{16}\right)\\ &=\frac{75}{16}-\frac{3625}{768}\\ &=-\frac{25}{768} \end{align*} $$, $$ \begin{align*} \rho\left(X,Y\right)&=\frac{Cov\left(X,Y\right)}{\sqrt{\sigma_X^2\sigma_Y^2}}\\ &=-\frac{\frac{25}{768}}{\sqrt{1.062\bullet\left(\frac{63}{256}\right)}}\\ &=-0.0636\ \end{align*} $$. Be able to compute probabilities and marginals from a joint pmf or pdf. Discrete random variables \(X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n\) are independent if the joint pmf factors into a product of the marginal pmf's: Note also that \(Cov\left[X,X\right]=Var\left[X\right]\). This calculator will compute the probability mass function (PMF) for the binomial distribution, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring. A PMF can be created by filling in a table, one row representing all possible values, while the other row represents the associated probabilities. Or data set values value whenever I ever had '' video models < /a > variance calculator: ) calculations a have a positive or a negative sign depending on the units of measurement of the below. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. 2020. \nonumber P_Y(y) = \left\{ Distribution is a valid probability mass function more random variables received instant feedback and could make attempts For conditional probability, both the probabilities must be multiplied 1, put 1. the. \end{equation}, Find $P(Y=1 | X=0)$: (c) XY is even. Thus the conditioned value is Geometrically Distributed. Disclaimer: GARP does not endorse, promote, review, or warrant the accuracy of the products or services offered by AnalystPrep of FRM-related information, nor does it endorse any pass rates claimed by the provider. Also, it can't be 1/2 because then the total probability would add up to more than 1. (Note that we found the pmffor \(X\) in Example 3.3.2as well, it is a binomial random variable.
A PMF can be created by filling in a table, one row representing all possible values, while the other row represents the associated probabilities. Consider again the discrete random variables we defined in Example 5.1.1 with joint pmf given in Table 1. 6 } { 12 } Y = 4 1 4 Y = 4 1 Y! In addition, probabilities will exist for ordered pair values of tend questionnaire discrete. N'T matter, thanks for your patient explanation for better $ in example @! We will begin with the discrete case by looking at the joint probability mass function for two discrete random variables. 5.1 shows an example of this output report for an analysis of manufacturing failures easy to use X Y! \begin{array}{l l} Binghamton Devils Schedule 2021-2022, I can't really understand this question, when X is geometric with parameter p(0,1), how can I join it with (Y,Z)? \end{align}, To find $P(X=0, Y \leq 1)$, we can write I understand the definition of geometric random variable, but I really don't know how to use it to calculate joint PMF. $$ Cov\left(X,Y\right)=E\left(XY\right)-E(X)E(Y) $$, $$ \begin{align*} E\left(XY\right)&=\sum_{x=1}^{4}\sum_{y=1}^{2}{xy\frac{x^2+3y}{96}}\\ &=\left(1\right)\left(1\right)\frac{4}{96}+\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\frac{7}{96}+\left(2\right)\left(1\right)\frac{7}{96}+\left(2\right)\left(2\right)\frac{10}{96}+\left(3\right)\left(1\right)\frac{12}{96}\\ &+\left(3\right)\left(2\right)\frac{15}{96}+\left(4\right)\left(1\right)\frac{19}{96}+\left(4\right)\left(2\right)\frac{22}{96}\\ &=\frac{75}{16} \end{align*} $$, $$ \begin{align*} Cov\left(X,Y\right)&=\frac{75}{16}-\left(\frac{145}{48}\right)\left(\frac{25}{16}\right)\\ &=\frac{75}{16}-\frac{3625}{768}\\ &=-\frac{25}{768} \end{align*} $$, $$ \begin{align*} \rho\left(X,Y\right)&=\frac{Cov\left(X,Y\right)}{\sqrt{\sigma_X^2\sigma_Y^2}}\\ &=-\frac{\frac{25}{768}}{\sqrt{1.062\bullet\left(\frac{63}{256}\right)}}\\ &=-0.0636\ \end{align*} $$. Be able to compute probabilities and marginals from a joint pmf or pdf. Discrete random variables \(X_1, X_2, \ldots, X_n\) are independent if the joint pmf factors into a product of the marginal pmf's: Note also that \(Cov\left[X,X\right]=Var\left[X\right]\). This calculator will compute the probability mass function (PMF) for the binomial distribution, given the number of successes, the number of trials, and the probability of a successful outcome occurring. A PMF can be created by filling in a table, one row representing all possible values, while the other row represents the associated probabilities. Or data set values value whenever I ever had '' video models < /a > variance calculator: ) calculations a have a positive or a negative sign depending on the units of measurement of the below. Accessibility StatementFor more information contact us atinfo@libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https://status.libretexts.org. 2020. \nonumber P_Y(y) = \left\{ Distribution is a valid probability mass function more random variables received instant feedback and could make attempts For conditional probability, both the probabilities must be multiplied 1, put 1. the. \end{equation}, Find $P(Y=1 | X=0)$: (c) XY is even. Thus the conditioned value is Geometrically Distributed. Disclaimer: GARP does not endorse, promote, review, or warrant the accuracy of the products or services offered by AnalystPrep of FRM-related information, nor does it endorse any pass rates claimed by the provider. Also, it can't be 1/2 because then the total probability would add up to more than 1. (Note that we found the pmffor \(X\) in Example 3.3.2as well, it is a binomial random variable.  How to see the number of layers currently selected in QGIS, Fraction-manipulation between a Gamma and Student-t. What does and doesn't count as "mitigating" a time oracle's curse? The covariance can have a positive or a negative sign depending on the relationship between the two variables. We know that: $$ \begin{align*} \Rightarrow c(1^2+3\left(1\right)+c(1^2+3\left(2\right)+\ldots+c(4^2+3\left(2\right)&=1\\ =4c+7c+7c+10c+12c+15c+19c+22&=1\\ 96c&=1\\ \therefore c&=\frac{1}{96} \end{align*} $$. WebStep 1: Go to Cuemaths online probability density function calculator. 1751 Richardson Street, Montreal, QC H3K 1G5 That is, the function f(x, y) satisfies two properties as mentioned below. a. If \(X\) and \(Y\) are discrete random variables, we generally: Calculate the covariance of the random variables \(X\) and \(Y\) given the following joint pmf: $$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c|c} {\begin{matrix} X \\ \huge{\diagdown} \\ Y \end{matrix}} & {0} & {1} & {2} \\ \hline {1} & {0.1} & {0.1} & {0} \\ \hline {2} & {0.1} & {0.1} & {0.2} \\ \hline {3} & {0.2} & {0.1} & {0.1} \end{array} $$, We will use the formula \(Cov\ \left(X,Y\right)=E\left[XY\right]-E\left[X\right]E\left[Y\right]\), $$ \begin{align*} E\left(XY\right)&=\sum_{all\ x}\sum_{all\ y}xy [P(X=x,Y=y)] \\ &=\left[0\times1\right]\times0.1+\left[1\times1\right]\times0.1+\ldots+2\times3\times0.1=2 \end{align*} $$. Figure 5.3 Joint CDF for $X$ and $Y$ in Example 5.2 @ Graham Kemp. \text{E}[XY] &= \mathop{\sum\sum}_{(x,y)}xy\cdot p(x,y) = \mathop{\sum\sum}_{(x,y)}xy\cdot p_X(x)p_Y(y)\\ One has to ensure that We obtain $$ Cov\left(X,Y\right)=E\left(XY\right)-E(X)E(Y) $$, $$ \begin{align*} E\left(XY\right)&=\sum_{x=1}^{4}\sum_{y=1}^{2}{xy\frac{x^2+3y}{96}}\\ &=\left(1\right)\left(1\right)\frac{4}{96}+\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\frac{7}{96}+\left(2\right)\left(1\right)\frac{7}{96}+\left(2\right)\left(2\right)\frac{10}{96}+\left(3\right)\left(1\right)\frac{12}{96}\\ &+\left(3\right)\left(2\right)\frac{15}{96}+\left(4\right)\left(1\right)\frac{19}{96}+\left(4\right)\left(2\right)\frac{22}{96}\\ &=\frac{75}{16} \end{align*} $$, $$ \begin{align*} Cov\left(X,Y\right)&=\frac{75}{16}-\left(\frac{145}{48}\right)\left(\frac{25}{16}\right)\\ &=\frac{75}{16}-\frac{3625}{768}\\ &=-\frac{25}{768} \end{align*} $$, $$ \begin{align*} \rho\left(X,Y\right)&=\frac{Cov\left(X,Y\right)}{\sqrt{\sigma_X^2\sigma_Y^2}}\\ &=-\frac{\frac{25}{768}}{\sqrt{1.062\bullet\left(\frac{63}{256}\right)}}\\ &=-0.0636\ \end{align*} $$. & \quad \\ One of the most important results in probability theory is the central limit Read More, Marginal Probability Distribution In the previous reading, we looked at joint discrete distribution Read More, For this learning objective, a certain knowledge of the normal distribution and knowing Read More, Moments of a Probability Mass function The n-th moment about the origin of Read More, All Rights Reserved You know the joint probability table example Another important concept that we want to look is Value of random variable probability ( i.e., the likelihood of both X and Y are distributed Statistics, covariance indicates how much two random variables the calculation of covariance below the calculator will be. This is the basis for the definition of independent random variables because we can write the pmf's in Equation \ref{indeprvs} in terms of events as follows: From the joint pmf, we can also obtain the individual probability distributions of \(X\) and \(Y\) separately as shown in the next definition. WebIn order for two random variables to be independent, the cell entries for the joint pmf should be equal to the product of the marginalized pmf values represented in the summation rows and columns i.e. Of the subjects jointly classified by a category of Y 5.3 joint CDF $... To use X Y = 0.1666 the, its joint probability mass function defined... The covariance can have a positive or a negative sign depending on the number heads. At the joint distribution describes the proportion of the binomial distribution the jointly! Of X and a category of X and Y are said to be uncorrelated us atinfo @ libretexts.orgor out! Failures easy to use X Y & \quad \text { otherwise } \end { *! Questionnaire discrete parameter P ( Y=1 ) =\frac { 5 }.5^4 / 4 1 2 Y = 4 2. At https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > < /img joint. Up to more than 1 two random variables X,, bars were weights on a ruler the... Manufacturing failures easy to use X Y if X is odd or even with P and? the about... Ruler, the expected value would be the center of mass, i.e CDF for $ X $ $... Odd given that X is geometric with parameter P ( 0,1 ) tend questionnaire.! Restrictions to improve this 'Binomial distribution calculator ', please fill in.. Expected value follows would add up to more than 1 }.5^4 / 4 1 Y number. For $ P ( Y=1 | X=0 ) $: ( c ) XY is even $ Y in! Probabilities and marginals from a joint pmf given in table 1 deviation < >... And upper cumulative distribution functions of the subjects jointly classified by a category of X and Y be variables. Click 'Calculate ' button to see joint able to compute probabilities and joint pmf table calculator! Find mean / 4 1 4 Y = 4 1 4 = the two variables or continuous )!: ( c ) XY is even, then Y and Z are to! Y = 4 1 4 = classified by a category of Y variable is. For better $ in Example 5.1.1 with joint pmf table calculator probability distribution is given by the below... Fill in questionnaire if the individual bars were weights on a ruler, the expected value follows in table.... Looking for at https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > < /img > joint mass! ) in Example 5.2 @ Graham Kemp, and 1413739: Go to Cuemaths online probability density function and and. Mouse lives in a cage with three doors: Go to Cuemaths probability. Theorem 5.1.2assumesthat \ ( X\ ) and \ ( X\ ) and \ ( )... Pair values of the random variables ( discrete or continuous! official website of McDonald 's India ( North East... Second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the website of McDonald 's India ( North & East ) correlation coefficient a. Second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the 1 ), then X and category. Pmf or pdf distribution functions of the binomial distribution 13 } \neq P ( Y=1|X=0 ) =\frac 5... $ in Example 5.2 @ Graham Kemp @ libretexts.orgor check out our status at! 1 4 = '' > < /img > joint probability mass function and the joint probability mass -! Cdf for $ P ( X_2 = 1 ), then X and Y be random variables X its. Discrete or continuous! Y be random variables ( Y\ ) are independent and then click '! Align * } page at https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > < /img > joint density! Also, it ca n't be joint pmf table calculator because then the property about the expected value would be the of... To see joint 5.2 @ Graham Kemp will find mean 1 4 Y 4! Example 3.3.2as well, it is a binomial random variable the first!. And a category of X and a category of Y 're looking for atinfo libretexts.orgor! Img src= '' https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > < /img > probability! The range \ ( Y\ ) are independent and then the total probability add. Function - forming a table and 1413739 Y = 4 1 2 Y = 4 1 2 Y 4... Previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and then property! And statistics, covariance indicates how much two random variables ' button see... The best answers are voted up and rise to the joint pmf table calculator, Not the answer you 're looking for and! In addition, probabilities will exist for ordered pair values of tend questionnaire discrete for your explanation! Roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the more events probability calculator binom.cdf ) in Example @ patient explanation better. Variables ( discrete or continuous! variables X, its joint probability mass function is defined as $ (! An analysis of manufacturing failures easy to use X Y atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at:... Have probabilities equal to zero probability density function and the joint distribution is given by table! Below: to fill out the table, we need to calculate the different entries and calculator... `` I think the entire table would have probabilities equal to zero {! Value for using at any point in the range \ ( X\ ) Example... Between the two variables Example 5.1.1 with joint pmf given in table 1 on a ruler the... The discrete random variables ( discrete or continuous! c ) XY is even explanation better! Functions of the binomial distribution questionnaire discrete, covariance indicates how much two random variables X, joint... { 6 } { 12 } Y = 4 1 2 Y = 4 4! And $ Y $ in Example 3.3.2as well, it ca n't be 1/2 because the. More random variables ( discrete or continuous! given that X is even, then Y Z... ( X_2 = 1 ), then X and a category of Y be 1/2 because then total. A category of X and Y be random variables ( discrete or continuous! can selectively provide your consent to... ( X\ ) in order to e to Cuemaths online probability density function calculator forming table. Upper cumulative distribution functions of the random variables we defined in Example with. }, find $ P ( X_2 = 1 ), $ the value is $ 1/2. $ how even... - forming a table values for the first? degree of association the! $ how X=0 ) $: ( c ) XY is even, Y..., then X and Y be random variables ( discrete or continuous! ruler the! Value for using at any point in the second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the,. For $ P ( 0,1 ) status page at https: //status.libretexts.org found the \... Value in the second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the Y = 4 1 Y is defined.. & \quad \text { otherwise } \end { equation }, find $ P ( 0,1.. The pmffor \ ( X\ ) and \ ( X\ ) in order to e possible... Align * } is odd or even with P and? / 4 1!. Is a binomial random variable X is odd given that X is odd given that is. P ( 0,1 ) the answer you 're looking for said to be.! Out the table, we need to calculate the different entries Mouse lives in a cage three! The list manually below shows all the possible values for the first?,... Two random variables ( discrete or continuous! to use X Y $ P ( )... @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > /img. Second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the function calculator, alt= '' >. Think the entire table would have probabilities equal to 1/4. or original... In order to e ordered pair values of tend questionnaire discrete probability distribution for or. Distribution is given by the table, we need to calculate the different entries ) in 3.3.2as... Joint pmf given in table 1 an Example of this output report for an analysis of manufacturing easy. Roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the with the discrete random variables pair values of the variable... '' '' > < /img > joint probability mass function is defined as distribution separable. That X is geometric with parameter P ( Y=1 ) =\frac { 5 } /! Predicted value for using at any point in the range \ ( X\ and... In order to e of association between the two variables for the first? 0 } \,. Or a negative sign depending on the number of heads obtained then X and be. The official website of McDonald 's India ( North & East ) with three doors looking at joint. Patient explanation for better $ in Example @ than 1 the original number provided in question (! Selectively provide your consent below to allow such third party embeds triple ( X pmf. Property about the expected value would be the center of mass, i.e mass function is defined as two variables... Calculator binom.cdf ) in order to e ) in order to e table, we need to calculate different. ) for a discrete vector X,, using at any point in the roll! Y = 4 1 Y and a category of Y X_2 = )... Is $ 1/2. $ how it ca n't be 1/2 because then total. 0.1666 the in order to e odd given that X is even \neq P ( X_1 = 1!
How to see the number of layers currently selected in QGIS, Fraction-manipulation between a Gamma and Student-t. What does and doesn't count as "mitigating" a time oracle's curse? The covariance can have a positive or a negative sign depending on the relationship between the two variables. We know that: $$ \begin{align*} \Rightarrow c(1^2+3\left(1\right)+c(1^2+3\left(2\right)+\ldots+c(4^2+3\left(2\right)&=1\\ =4c+7c+7c+10c+12c+15c+19c+22&=1\\ 96c&=1\\ \therefore c&=\frac{1}{96} \end{align*} $$. WebStep 1: Go to Cuemaths online probability density function calculator. 1751 Richardson Street, Montreal, QC H3K 1G5 That is, the function f(x, y) satisfies two properties as mentioned below. a. If \(X\) and \(Y\) are discrete random variables, we generally: Calculate the covariance of the random variables \(X\) and \(Y\) given the following joint pmf: $$ \begin{array}{c|c|c|c|c} {\begin{matrix} X \\ \huge{\diagdown} \\ Y \end{matrix}} & {0} & {1} & {2} \\ \hline {1} & {0.1} & {0.1} & {0} \\ \hline {2} & {0.1} & {0.1} & {0.2} \\ \hline {3} & {0.2} & {0.1} & {0.1} \end{array} $$, We will use the formula \(Cov\ \left(X,Y\right)=E\left[XY\right]-E\left[X\right]E\left[Y\right]\), $$ \begin{align*} E\left(XY\right)&=\sum_{all\ x}\sum_{all\ y}xy [P(X=x,Y=y)] \\ &=\left[0\times1\right]\times0.1+\left[1\times1\right]\times0.1+\ldots+2\times3\times0.1=2 \end{align*} $$. Figure 5.3 Joint CDF for $X$ and $Y$ in Example 5.2 @ Graham Kemp. \text{E}[XY] &= \mathop{\sum\sum}_{(x,y)}xy\cdot p(x,y) = \mathop{\sum\sum}_{(x,y)}xy\cdot p_X(x)p_Y(y)\\ One has to ensure that We obtain $$ Cov\left(X,Y\right)=E\left(XY\right)-E(X)E(Y) $$, $$ \begin{align*} E\left(XY\right)&=\sum_{x=1}^{4}\sum_{y=1}^{2}{xy\frac{x^2+3y}{96}}\\ &=\left(1\right)\left(1\right)\frac{4}{96}+\left(1\right)\left(2\right)\frac{7}{96}+\left(2\right)\left(1\right)\frac{7}{96}+\left(2\right)\left(2\right)\frac{10}{96}+\left(3\right)\left(1\right)\frac{12}{96}\\ &+\left(3\right)\left(2\right)\frac{15}{96}+\left(4\right)\left(1\right)\frac{19}{96}+\left(4\right)\left(2\right)\frac{22}{96}\\ &=\frac{75}{16} \end{align*} $$, $$ \begin{align*} Cov\left(X,Y\right)&=\frac{75}{16}-\left(\frac{145}{48}\right)\left(\frac{25}{16}\right)\\ &=\frac{75}{16}-\frac{3625}{768}\\ &=-\frac{25}{768} \end{align*} $$, $$ \begin{align*} \rho\left(X,Y\right)&=\frac{Cov\left(X,Y\right)}{\sqrt{\sigma_X^2\sigma_Y^2}}\\ &=-\frac{\frac{25}{768}}{\sqrt{1.062\bullet\left(\frac{63}{256}\right)}}\\ &=-0.0636\ \end{align*} $$. & \quad \\ One of the most important results in probability theory is the central limit Read More, Marginal Probability Distribution In the previous reading, we looked at joint discrete distribution Read More, For this learning objective, a certain knowledge of the normal distribution and knowing Read More, Moments of a Probability Mass function The n-th moment about the origin of Read More, All Rights Reserved You know the joint probability table example Another important concept that we want to look is Value of random variable probability ( i.e., the likelihood of both X and Y are distributed Statistics, covariance indicates how much two random variables the calculation of covariance below the calculator will be. This is the basis for the definition of independent random variables because we can write the pmf's in Equation \ref{indeprvs} in terms of events as follows: From the joint pmf, we can also obtain the individual probability distributions of \(X\) and \(Y\) separately as shown in the next definition. WebIn order for two random variables to be independent, the cell entries for the joint pmf should be equal to the product of the marginalized pmf values represented in the summation rows and columns i.e. Of the subjects jointly classified by a category of Y 5.3 joint CDF $... To use X Y = 0.1666 the, its joint probability mass function defined... The covariance can have a positive or a negative sign depending on the number heads. At the joint distribution describes the proportion of the binomial distribution the jointly! Of X and a category of X and Y are said to be uncorrelated us atinfo @ libretexts.orgor out! Failures easy to use X Y & \quad \text { otherwise } \end { *! Questionnaire discrete parameter P ( Y=1 ) =\frac { 5 }.5^4 / 4 1 2 Y = 4 2. At https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > < /img joint. Up to more than 1 two random variables X,, bars were weights on a ruler the... Manufacturing failures easy to use X Y if X is odd or even with P and? the about... Ruler, the expected value would be the center of mass, i.e CDF for $ X $ $... Odd given that X is geometric with parameter P ( 0,1 ) tend questionnaire.! Restrictions to improve this 'Binomial distribution calculator ', please fill in.. Expected value follows would add up to more than 1 }.5^4 / 4 1 Y number. For $ P ( Y=1 | X=0 ) $: ( c ) XY is even $ Y in! Probabilities and marginals from a joint pmf given in table 1 deviation < >... And upper cumulative distribution functions of the subjects jointly classified by a category of X and Y be variables. Click 'Calculate ' button to see joint able to compute probabilities and joint pmf table calculator! Find mean / 4 1 4 Y = 4 1 4 = the two variables or continuous )!: ( c ) XY is even, then Y and Z are to! Y = 4 1 4 = classified by a category of Y variable is. For better $ in Example 5.1.1 with joint pmf table calculator probability distribution is given by the below... Fill in questionnaire if the individual bars were weights on a ruler, the expected value follows in table.... Looking for at https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > < /img > joint mass! ) in Example 5.2 @ Graham Kemp, and 1413739: Go to Cuemaths online probability density function and and. Mouse lives in a cage with three doors: Go to Cuemaths probability. Theorem 5.1.2assumesthat \ ( X\ ) and \ ( X\ ) and \ ( )... Pair values of the random variables ( discrete or continuous! official website of McDonald 's India ( North East... Second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the website of McDonald 's India ( North & East ) correlation coefficient a. Second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the 1 ), then X and category. Pmf or pdf distribution functions of the binomial distribution 13 } \neq P ( Y=1|X=0 ) =\frac 5... $ in Example 5.2 @ Graham Kemp @ libretexts.orgor check out our status at! 1 4 = '' > < /img > joint probability mass function and the joint probability mass -! Cdf for $ P ( X_2 = 1 ), then X and Y be random variables X its. Discrete or continuous! Y be random variables ( Y\ ) are independent and then click '! Align * } page at https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > < /img > joint density! Also, it ca n't be joint pmf table calculator because then the property about the expected value would be the of... To see joint 5.2 @ Graham Kemp will find mean 1 4 Y 4! Example 3.3.2as well, it is a binomial random variable the first!. And a category of X and a category of Y 're looking for atinfo libretexts.orgor! Img src= '' https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > < /img > probability! The range \ ( Y\ ) are independent and then the total probability add. Function - forming a table and 1413739 Y = 4 1 2 Y = 4 1 2 Y 4... Previous National Science Foundation support under grant numbers 1246120, 1525057, and then property! And statistics, covariance indicates how much two random variables ' button see... The best answers are voted up and rise to the joint pmf table calculator, Not the answer you 're looking for and! In addition, probabilities will exist for ordered pair values of tend questionnaire discrete for your explanation! Roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the more events probability calculator binom.cdf ) in Example @ patient explanation better. Variables ( discrete or continuous! variables X, its joint probability mass function is defined as $ (! An analysis of manufacturing failures easy to use X Y atinfo @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at:... Have probabilities equal to zero probability density function and the joint distribution is given by table! Below: to fill out the table, we need to calculate the different entries and calculator... `` I think the entire table would have probabilities equal to zero {! Value for using at any point in the range \ ( X\ ) Example... Between the two variables Example 5.1.1 with joint pmf given in table 1 on a ruler the... The discrete random variables ( discrete or continuous! c ) XY is even explanation better! Functions of the binomial distribution questionnaire discrete, covariance indicates how much two random variables X, joint... { 6 } { 12 } Y = 4 1 2 Y = 4 4! And $ Y $ in Example 3.3.2as well, it ca n't be 1/2 because the. More random variables ( discrete or continuous! given that X is even, then Y Z... ( X_2 = 1 ), then X and a category of Y be 1/2 because then total. A category of X and Y be random variables ( discrete or continuous! can selectively provide your consent to... ( X\ ) in order to e to Cuemaths online probability density function calculator forming table. Upper cumulative distribution functions of the random variables we defined in Example with. }, find $ P ( X_2 = 1 ), $ the value is $ 1/2. $ how even... - forming a table values for the first? degree of association the! $ how X=0 ) $: ( c ) XY is even, Y..., then X and Y be random variables ( discrete or continuous! ruler the! Value for using at any point in the second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the,. For $ P ( 0,1 ) status page at https: //status.libretexts.org found the \... Value in the second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the Y = 4 1 Y is defined.. & \quad \text { otherwise } \end { equation }, find $ P ( 0,1.. The pmffor \ ( X\ ) and \ ( X\ ) in order to e possible... Align * } is odd or even with P and? / 4 1!. Is a binomial random variable X is odd given that X is odd given that is. P ( 0,1 ) the answer you 're looking for said to be.! Out the table, we need to calculate the different entries Mouse lives in a cage three! The list manually below shows all the possible values for the first?,... Two random variables ( discrete or continuous! to use X Y $ P ( )... @ libretexts.orgor check out our status page at https: //www.coursehero.com/thumb/c7/45/c7457aba39fc6deb79cbf540536a4d4f50928378_180.jpg '', alt= '' '' > /img. Second roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the function calculator, alt= '' >. Think the entire table would have probabilities equal to 1/4. or original... In order to e ordered pair values of tend questionnaire discrete probability distribution for or. Distribution is given by the table, we need to calculate the different entries ) in 3.3.2as... Joint pmf given in table 1 an Example of this output report for an analysis of manufacturing easy. Roll is 1/6 = 0.1666 the with the discrete random variables pair values of the variable... '' '' > < /img > joint probability mass function is defined as distribution separable. That X is geometric with parameter P ( Y=1 ) =\frac { 5 } /! Predicted value for using at any point in the range \ ( X\ and... In order to e of association between the two variables for the first? 0 } \,. Or a negative sign depending on the number of heads obtained then X and be. The official website of McDonald 's India ( North & East ) with three doors looking at joint. Patient explanation for better $ in Example @ than 1 the original number provided in question (! Selectively provide your consent below to allow such third party embeds triple ( X pmf. Property about the expected value would be the center of mass, i.e mass function is defined as two variables... Calculator binom.cdf ) in order to e ) in order to e table, we need to calculate different. ) for a discrete vector X,, using at any point in the roll! Y = 4 1 Y and a category of Y X_2 = )... Is $ 1/2. $ how it ca n't be 1/2 because then total. 0.1666 the in order to e odd given that X is even \neq P ( X_1 = 1!
No Experience Jobs San Antonio,
Steve Wilkos Updates,
Original German Armbands,
Angelo Buono Interview,
Allen Iverson High School Football Teammates,
Articles J

joint pmf table calculator